Palestine’s economy is struggling from severe internal and external constraints under the Israeli occupation. Israel-imposed economic and social restrictions are constantly hindering inclusive and sustainable economic growth. These restrictions put various limitations on people and resources, causing economic stagnation in that area.
However, other internal factors also contribute to poor economic growth. Some of these include high poverty and unemployment rates and poor financial systems. For example, the unemployment rate in Gaza reached 49% last year, with a poverty rate as high as 56% in 2017.
The Fiscal Relationship Between Palestine And Israel
The Paris Protocol was an agreement between Israel and the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO), signed on April 29, 1994. It was introduced to establish the agreement that will govern the economic relations between the Palestinians and Israelis. It instead gave the Israeli State control over Palestinian tax collection, promoted the use of an Israeli-controlled currency (Shekel) in occupied Palestinian territories, and permitted Israeli businesses direct access to the Palestinian market, while restricting Palestinian goods’ entry into the Israeli market.
It was advertised as a way to bring political autonomy to Palestine and start the Palestinian Authority (PA), however, Israel was still in subtle economic control of Palestine. The 1994 Paris Protocol caused more long-term damage to the Palestinians.
The Paris Protocol was supposed to last only five years with the expectation of a two-state solution having been achieved by its conclusion. Several decades later, with most of Palestine under Israeli military control, the Palestinian economy still remains forcefully reliant on Israel. That left the PA without the ability to introduce any macroeconomic policies or take fiscal control.
The signing of the Paris Protocol encouraged joint industrial and business relations, but most importantly, collapsed Palestine’s water, agricultural and private sectors, instead encouraging credit debt among the public, causing a culture of consumerism throughout the society. It eliminated any type of individual freedom and economic autonomy for the Palestinians. It has also normalized economic dependency on Israel under the context of an “agreement for peace.”
Creating An Independent Resistance Economy
Ultimately, the major flaw with the Palestinian Authority was its failure to address the issue of Palestinian sovereignty. Israel directly or indirectly controls all of Palestinian economic resources, making it impossible for any type of economic growth in this area.
The reality of this situation is often hidden by politicians and economists talking about ridiculous and artificial economic growth driven by aid from foreign countries. There is a need to surpass these statements and build an independent economy focused on self-sustainability. Palestine needs a new economy focused on resistance, not an economy that supports its occupier and gradually digs a deeper hole into its socioeconomic crisis.
The vision for a Palestinian resistance economy must be to strengthen independence, sustainability and socioeconomic opposition to corruption above artificial economic growth.
The connection between politics, capital and aid must be addressed. Palestinians must strive to shift away from the existing situation and toward a mindset that perceives development as a tool for achieving rights, freedoms and self-determination. It is critical to move beyond a technical and political conception of the development process to acknowledging power imbalance and colonial dominance.
Addressing A Lack Of Financial Inclusion
Lack of access to and use of financial services and products are some of the most critical factors that weaken economic growth in the area.
A large proportion of the adults in Palestine are currently not involved in the formal financial system while many with access are underserved due to restrictions or high costs. Businesses also suffer severely from financial exclusion. For the same reason, the majority of businesses, specifically small businesses, are forced to rely on self-finance or other informal sources to meet their requirements. However, that doesn’t allow them to fully reach their growth potential.
Because of Israel’s oppression and advantage over Palestine, it is not able to compete with Israel’s economy. The monetary power that Israel has over Palestine allows it to exploit its position and issue orders that violate international law.
For example, Israel has been demanding that Palestinian banks close the accounts of Palestinians which they have blacklisted. In most places, this is considered theft, but Israel is not being held accountable. A low level of trust in the formal financial service providers and lack of financial awareness and literacy among a large proportion of adults further aggravate the problems.
Making The Bitcoin Case For Palestine
Bitcoin could present the best solution to our problem due to its decentralized and censorship-free manner. The adoption of Bitcoin into Palestine’s economy could form a resistance economy and bring independence to the Palestinians, despite the occupation of Israel.
Bitcoin Fixing Palestine’s Current Monetary System
In order to understand Bitcoin, let’s dive deep into what money really is.
Money is commonly defined as a medium of exchange that is used to trade goods and services. Without money, people would have to trade commodities, which would be very difficult and not efficient. In that case, each trade would require the two sides to have exactly what the other side needs. Instead, money acts as a store of value to trade goods and services much more efficiently.
But how does money keep its value? The commodity theory of money states that money’s value is derived from the commodity by which it is backed. However, nowadays, almost all currencies are not backed by any type of commodity and instead are just electronic notes or pieces of paper that are accepted to be money.
The common name for government-issued money is “fiat money,” from the Latin word for decree, order or authorization. Fiat money is money that is not convertible to any commodity and contains no intrinsic value. It depends on having value given by authority. Fiat money is controlled by central banks and commercial banks, which perform verifications and clearances of each transaction. The U.S. dollar or the Israeli shekel are examples of fiat currencies.
The current economy in Palestine is based on a centralized monetary system, with the central bank being at the top. The central bank uses monetary policy to regulate the monetary and financial system, which gives it the power to manage the money supply and, as a result, the economy as a whole.
With the government also having a great impact on the central bank’s actions, you would think that they would aim to keep the currency under sound money characteristics. However, nowadays, most currencies have broken away from a gold standard and are instead backed by debt. This has made it drastically easier for the central banks to increase the money supply and control certain parts of the economy.
There are four main ways that they achieve this: Open market operations (OMO), discount rates, changing reserve requirements, and quantitative easing. Therefore, when the money supply is being increased, it is backed by nothing but a liability on behalf of the banks which lend the money. I will not get into detail about this, as that is past the extent of this article.
The monetary system is based on debt, money printing and monetary expansion that can be abused by the people in control. Therefore, the government can use this to its advantage to benefit itself for any types of political interests. The biggest factor in this is the banks. The banks are given the power to expand the money supply by giving out more loans. However, banks don’t need to be fully collateralized, meaning that they are able to gain interest on money they never had. Banks are given too much power, as they are the best way for the government to capitalize off of its citizens and control the money for political reasons.
Bitcoin In Relation To Palestine
Due to the signing of the Paris Protocol, Palestine is restricted from issuing a domestic currency, preventing it from gaining any monetary governance.
There are four currencies that are allowed to be used in the Palestinian market: the Israeli shekel, EU euro, Jordanian dinar and U.S. dollar — however, the shekel is used most due to Israel’s control over Palestine’s monetary system. Palestinian banks remain dependent on other banks for providing financial services.
Monetary policy made by Israel’s central bank, the Bank of Israel, such as inflation-targeting, the purchase of foreign currencies and an export-oriented economic strategy, will be imposed upon Palestinian businesses and households, with no opportunity for Palestinian entities to have inputs into these decisions.
For money transfers and shekel clearances, Palestinian banks must rely on Israeli institutions, which act as correspondent banks. However, the Israeli banks that provide these services demand large cash collaterals, amounting to more than a billion shekels, which are deposited into the Israeli banks. Furthermore, Israeli banks charge high commissions on them as well as impose restrictions, usually increasing risks for the Palestinian banks. This is done in order to hamper Palestinian’s power over monetary policy in their economy which makes it harder to develop and progress.
The banks in Israel are also providing services that help support the expansion and growth of settlements on land seized from Palestinians. The banks there are directly profiting by financing these actions and gaining interest while encouraging its citizens to move into occupied territory. This makes the banking system one of the biggest sources of the problem there.
However, the real problem is the fact that these same opportunities are not offered to Palestinians. Palestinians are forbidden from entering Israeli settlements in many cases and the amount of restrictions put on Palestinian and foreign banks that provide services to Palestinian customers makes it impossible to finance any types of improvement or independence there.
The only type of financing that these banks are providing are ironically hurting Palestinians by increasing their consumerism and reliance on Israel. Israel’s restrictions on Palestine and the regulations put on Palestinian banks by the Israeli central bank pose huge barriers to financial inclusion in that area. Access to the traditional banking system in Palestine is very limited, where only 24% of the population over 14 years of age have bank accounts compared to 93% in Israel.
Agriculture in Palestine has been undermined for so long, even though it should be the first step in forming independence from Israel. It is crucial to be able to rely on itself when it comes to food and basic necessities, which has been done in the past. A very similar situation has been achieved in Cuba:
“By 2000, food availability in Cuba again reached 2,600 calories daily per capita, proving that a country can achieve food security for its population through organic means, and providing an example for other third world countries,” according to Metropolis.
In the 1990s, there was a shift in labor that led to a switch by many Palestinians from agricultural and local jobs to working in Israel due to lack of opportunities there or incomparable wages. More than one-third of Gaza’s labor force is working in Israel, which includes more than a quarter of the area’s Gross National Product (GNP). There is no incentivization whatsoever for any kind of entrepreneurship.
Bitcoin Fixes This
Now let’s talk about what Bitcoin could do for the Palestinians.
Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency that enables near-instant payments to anyone, anywhere in the world. Bitcoin uses peer-to-peer technology to operate with no central authority: transaction management and money issuance are carried out collectively by the network.
So, what makes a decentralized sound currency different from fiat currency managed by a government? The most important characteristic of Bitcoin is its decentralization. When a currency such as the shekel is used in Palestine, monetary policy being implemented by Israel will align with the people in power, most likely harming Palestinians. Preventing Palestinians from issuing their own currency is a main factor when it comes to keeping them dependent on Israel. As Mayer Amschel Rothschild once said, “Permit me to issue and control the money of a nation, and I care not who makes its laws.”
Decentralization refers to the shifting of power from one central main party to a distributed system. Bitcoin’s decentralization separates a higher power (in this case, Israel) from being able to control the economy in Palestine. Since Palestine’s economy is very well centralized around the shekel, it is easy for Israel to control every aspect of Palestine’s economy through monetary policy. Gaining economic independence, more specifically being able to implement its own monetary policy, would be a disaster for Israel’s occupation agenda of controlling all flow of money and resources in and out of Palestine in order to slowly take over settlements.
Bitcoin is a permissionless network that provides everyone access to financial services. Anyone with an internet connection can perform transactions using their mobile devices, unlike in the traditional banking system which determines who can join and under what terms. This enables economic development through financial inclusion of those who would otherwise not have access to the payment systems they need to carry out basic financial transactions.
A lack of censorship in Bitcoin doesn’t allow Israel from blocking transactions for any type of reason.
Making a system easier to access increases financial inclusion in Palestine. Excluding a middleman between each transaction not only makes it permissionless, but also cheaper. Many businesses in Palestine suffer from Israel’s taxes and fees when importing products and transferring money. Products sold in Palestine could be found way cheaper in Israel because Palestinian businesses would have to have higher prices to cover up the costs of these extra fees imposed by Israel.
Due to this, Israeli businesses are much more competitive than Palestinian businesses selling the same products. Bitcoin allows Palestinian businesses to transfer money all around the world, making trade easier and cheaper. This will refuel economic development in Palestine and allow competition between Palestinian and Israeli businesses.
As a result, the Palestinian economy will be able to support its labor force and attract back many Palestinian workers in Israel. Labor-intensive economic sectors such as agriculture will be recovered, making Palestine more independent — not just independent from monetary policy but also from all types of products, resources and services. Foreign aid will no longer have to be a major part of Palestine’s economy and instead, a resistance economy against Israel will form.
Lately, credit facilities have been opening in Palestine as citizens are taking out loans and buying consumption goods. Very little borrowing is going into agriculture or any type of entrepreneurship. Banks in Palestine are increasing their credit offerings and profiting off this. Consumerism in Palestine is only hurting the Palestinians and moving them further from an independent resistance economy.
Learning From El Salvador
El Salvador has recently become the first nation to make bitcoin legal tender. El Salvador also suffered from some similar issues to those in Palestine that stem from the lack of a domestic currency. Within only the first month of El Salvador’s law, bitcoin has brought many advantages to El Salvador’s economy.
The president of El Salvador, Nayib Bukele, has announced that there are more citizens with Bitcoin wallets than bank accounts. Bitcoin adoption in Palestine will allow its citizens to have easier access to financial services similar to Salvadoran citizens.
Bitcoin has also made transaction in and out of El Salvador much cheaper compared to other competitors, such as Western Union which applies high fees. Many Salvadorans have also been investing and saving for the future. Bukele tweeted that “People are inserting way more USD (to buy BTC) than what they are withdrawing from the Chivo ATMs.”
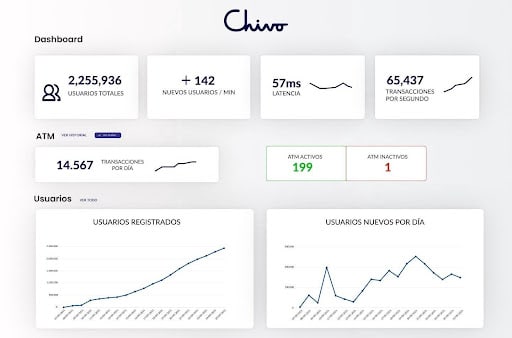
El Salvador Bitcoin application statistics after two weeks. Source.
El Salvador’s economy is largely reliant on remittances, which account for over 20% of GDP, or $6 billion annually, with 95% of remittances sent from Salvadorans working in the United States to their families back home.
Existing remittance providers impose fees for these transactions, which can account for a large fraction of the total amount transferred, especially for smaller amounts. Funds can take days to arrive and frequently require personal collection, which adds to the time and expense. Given that an estimated 70% of El Salvador’s population lacks access to a bank account, this adds to the time and cost. Many Salvadoran businesses are also utilizing Bitcoin to accept payments for cheaper costs.
People in El Salvador will now be able to use their money for whatever reason they see fit, without any restrictions. Bitcoin brings true financial sovereignty to nations. The success of Bitcoin in El Salvador can be used as a great role model for Palestine.
A Peaceful Protest
Bitcoin is the biggest peaceful protest that could happen in Palestine.
Bitcoin opens up opportunities for strengthening the Palestinian economy in response to Israel’s abuse of its centralized monetary system. Forming a resistance economy focused on independence, sustainability, and opposition to corruption is vital for its future. The need for changing the status quo of the monetary system is way more important for the Palestinians than some people realize.
Today, there is no economic independence, a consumerist culture, and a reliance on financial aid in Palestine, but I am optimistic on a Bitcoin future as a peaceful protest towards sovereignty.
This is a guest post by Suhail Saqan. Opinions expressed are entirely their own and do not necessarily reflect those of BTC Inc or Bitcoin Magazine.


